|
Main Electronics Circuits Circuit Math Smith Charts Pictures Arizona Scenic
Colorado
Life In Jersey |
 |
 |
 |
Remember that resistors in parallel become: 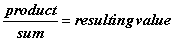
So in this circuit all we have to do is fill in the numbers. 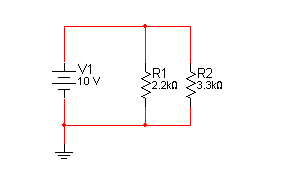
And we have this equation here 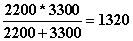
To get the current we use the same equation as before 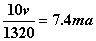
Keep in mind that when doing parallel combinations the voltage is going to be the same across all parallel lines. In our example we will have 10v in each resistor. This means that although we have a single value for the total resistance (1320), the current in each line will be different: 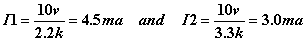
We can check this by adding up our currents 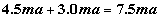
Note I rounded I1, which will explain the difference between 7.4ma and 7.5ma. Now lets play with Nodal Analysis Circuit Refresher | Series Resistors | Parallel Resistors | Nodal Analysis | Capacitors And Resistors | |
||
Copyright © 1999-2003 Jarg Dot Org
|